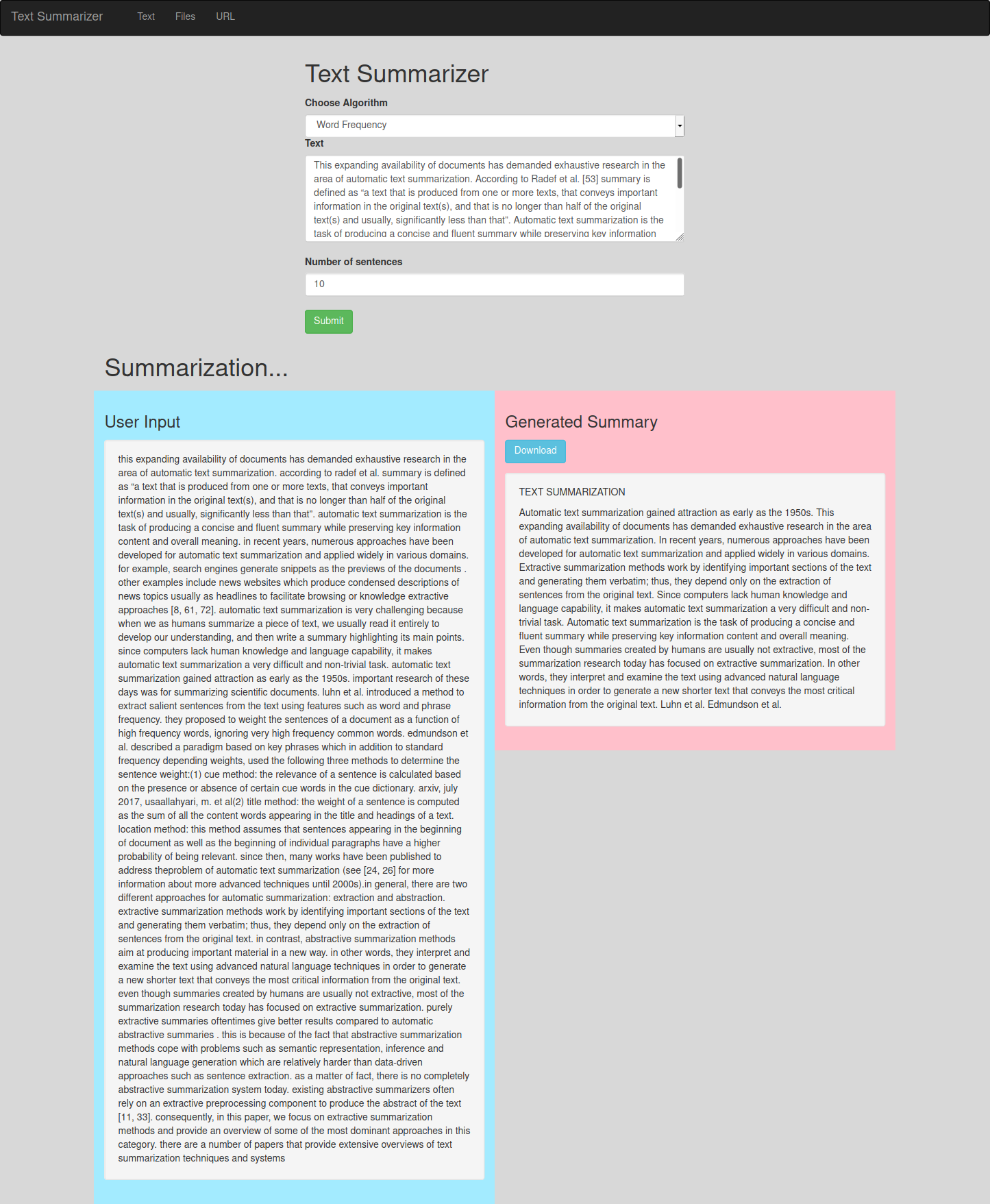
Extractive Text Summarizer
generating summaries from an input document while retaining the important points.
What is Text Summarization?
With push notifications and article digests gaining more and more traction, the task of generating intelligent and accurate summaries for long pieces of text has become a popular research as well as industry problem. Text summarization is the process of automatically generating summaries from an input document while retaining the important points. It would help in easy and fast retrieval of information.
There are two fundamental approaches to text summarization:
- Extractive summarization picks up sentences directly from the document based on a scoring function to form a coherent summary. This method work by identifying important sections of the text cropping out and stitch together portions of the content to produce a condensed version.
- Abstractive summarization systems generate new phrases, possibly rephrasing or using words that were not in the original text. Has complex capabilities like generalization, paraphrasing and incorporating real-world knowledge.
In this project, we have focused our work on Extractive summarization.

Algorithms Used
We have implemented three extractive text summarization algorithms - Word Frequency, Text Rank Algorithm and TF-IDF.
Word Frequency
---
1. Get input document and number of sentences in a summary(n)
2. Find the word tokens
3. Remove the stopwords
4. Calculate frequency of each word and create a word frequency table
5. Find the sentence tokens
6. Score the sentences by calculating term frequency
7. Generate summary - Display top n sentences based of sentence scores
---
Text Rank Algorithm
Text Rank is originally inspired from the PageRank algorithm. PageRank is used primarily for ranking web pages in online search results. Here, we consider sentences the equivalent of web pages, the probability of going from sentence A to sentence B is equal to the similarity of the 2 sentences.
---
1. Get input document and number of sentences in a summary(n)
2. Find the sentence tokens
3. Build a similarity matrix, here we have used Cosine similarity metrics
4. Apply the PageRank algorithm over this sentence graph
5. Order sentences by rank in descending order
6. Generate summary - Display top n sentences based of sentence scores
---
TF-IDF Algorithm
TF-IDF algorithm is made of 2 algorithms multiplied together. Term Frequency and Inverse document frequency Term frequency is how common a word is and inverse document frequency (IDF) is how unique or rare a word is.
Here we considered, number of documents as number of sentences.
-
Term frequency (TF)
\(TF(t) = \frac{Number\ of\ times\ term\ t\ appears\ in\ a\ document} {Total\ number\ of\ terms\ in\ the\ document}\) -
Inverse document frequency (IDF)
\(IDF(t) = log_e(\frac{Total\ number\ of\ documents }{Number\ of\ documents\ with\ term\ t\ in\ it})\) -
TF-IDF
\(TFIDF(t) = TF(t) * IDF(t)\)
Algorithm
---
1. Get input document and number of sentences in a summary(n)
2. Tokenize sentences
3. Create the Frequency matrix of the words in each sentence
4. Calculate Term Frequency and generate a matrix
5. Create a table for documents per words
6. Calculate IDF and generate a matrix
7. Calculate TF-IDF and generate a matrix
8. Score the sentences
9. Generate summary - Display top n sentences based of sentence scores
---
Technologies Used
- NLTK - The Natural Language Toolkit, or more commonly NLTK, is a suite of libraries and programs for symbolic and statistical natural language processing for English written in the Python programming language.
- Flask \& Flask-WT Forms - Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It supports extensions that can add application features as if they were implemented in Flask itself. Using Flask-WTF, we can define the form fields in our Python script and render them using an HTML template.
- Numpy - NumPy is a library for the Python programming language, adding support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large collection of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
- Beautiful Soup - Beautiful Soup is a Python package for parsing HTML and XML documents.
- Textract - This package provides a single interface for extracting content from any type of file, without any irrelevant markup.
Conclusion
We have used the basic Extractive Algorithms for implementing our project. Extractive summarization picks up sentences directly from the document based on a scoring function to form a coherent summary or we can say that it works by selecting the most meaningful sentences in an article and arranging them in a comprehensive manner. This means the summary sentences are extracted from the article without any modifications. The algorithms used in our project are Tf-Idf, Word-Frequency, and Text-Rank algorithm.
There are some use cases where automatic text summarization can be used across the enterprise. Some of them are: Search Marketing and SEO, Financial Research, Legal Contract Analysis, Medical Cases, Books and Literature, Help Desk and Customer Support.
The implemented algorithms are giving good results but there might be other approaches available as well to improve the accuracy. In future, we will explore the Abstractive Algorithms as well. Further based on the available datasets on Text Summarization, we will also calculate the BLEU score between a machine translation output and a human translation, to compare the accuracy of each algorithm.